On July 1, 1984, the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA) introduced a new rating that would fundamentally alter the landscape of American cinema: PG-13. This seemingly simple addition to the existing rating system emerged from mounting pressure by filmmakers, parents, and industry executives who recognized a critical gap in movie classification. The first film to carry this new designation, "Red Dawn," hit theaters that summer, marking the beginning of a new chapter in how Hollywood would approach storytelling, marketing, and audience targeting for decades to come.
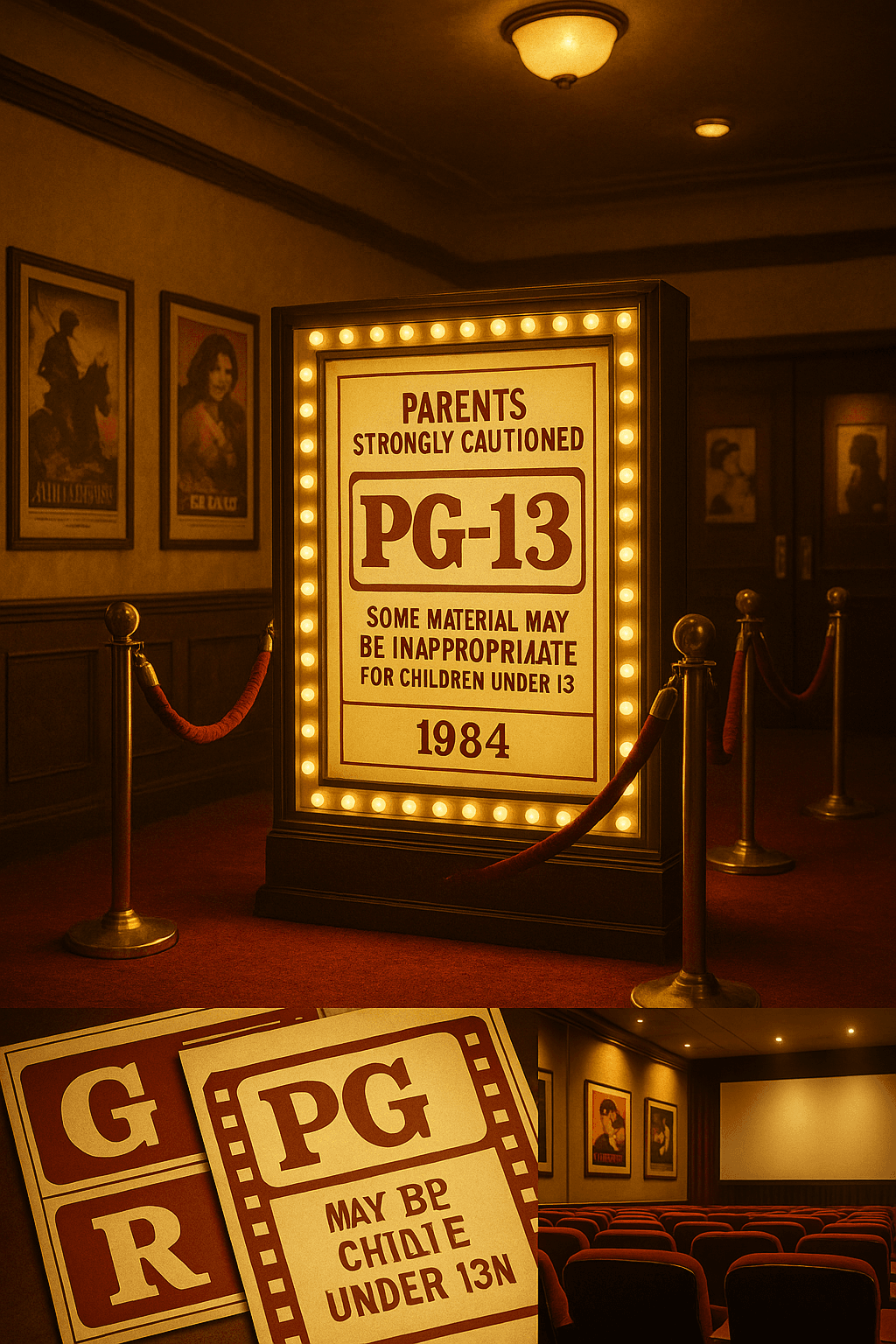
Before 1984, the MPAA's rating system operated with a significant blind spot. Films were classified as either G (suitable for all audiences), PG (parental guidance suggested), or R (restricted to viewers 17 and older unless accompanied by an adult). This structure left filmmakers in an impossible position when crafting stories that contained moderate violence, brief strong language, or mature themes that clearly exceeded PG standards but fell short of R-rated content.
The breaking point came with Steven Spielberg's "Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom" and "Gremlins," both released in 1984. These films received PG ratings despite containing intense violence and frightening scenes that many parents found inappropriate for younger children. Public outcry from parents, combined with advocacy from prominent directors like Spielberg himself, forced the MPAA to acknowledge that their system was inadequately serving both filmmakers and families.
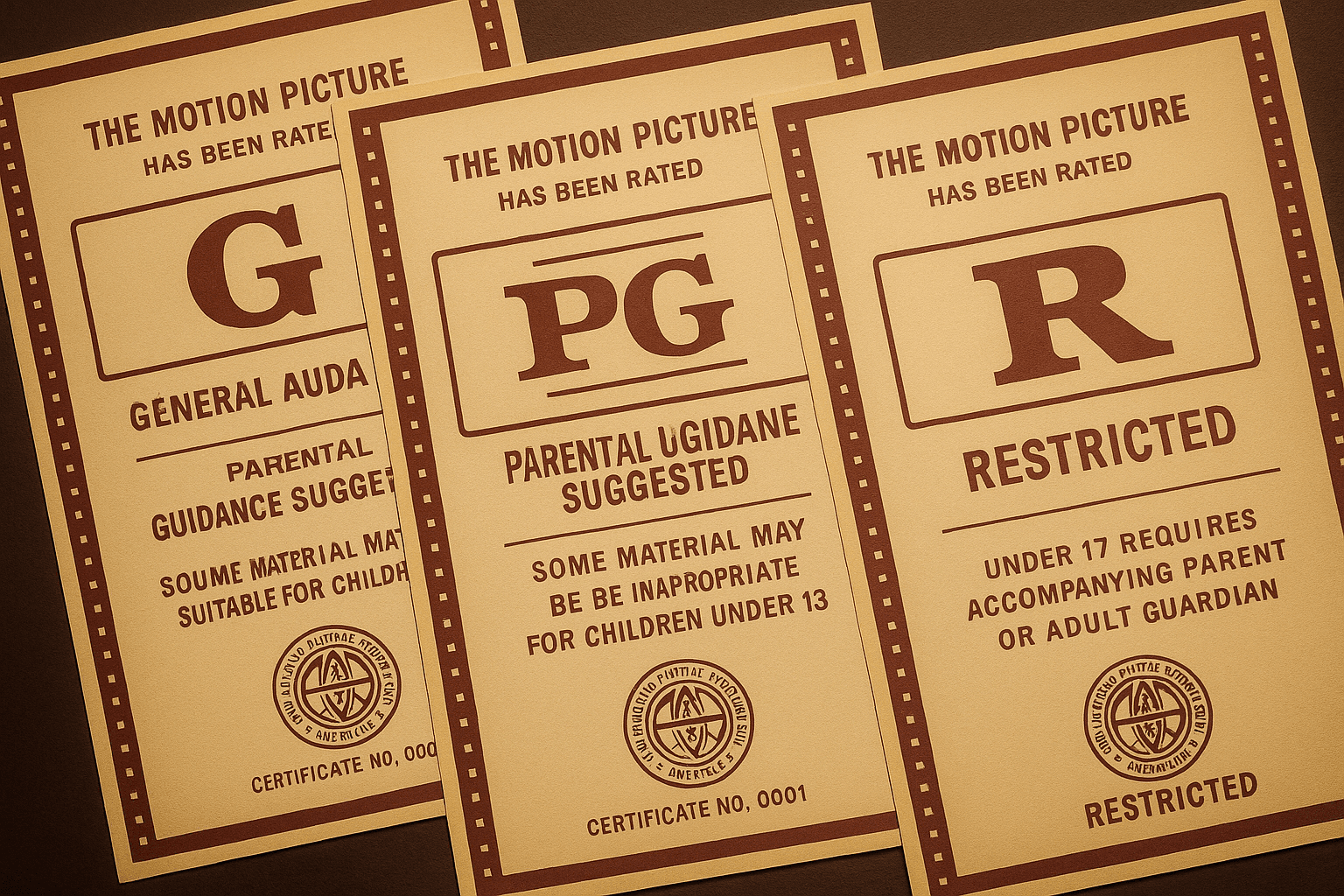
PG-13 quickly became the most commercially attractive rating in Hollywood, offering filmmakers the freedom to include more mature content while maintaining broad audience appeal. Unlike R-rated films, PG-13 movies could admit teenagers without adult supervision, immediately expanding the potential viewer base to include the lucrative adolescent demographic that drives much of the entertainment industry's revenue.
Major studios began specifically crafting films to achieve the PG-13 rating, sometimes editing content to avoid the more restrictive R rating while ensuring the film contained enough mature elements to appeal to older audiences. This strategic approach to content creation marked a fundamental shift in how Hollywood balanced artistic vision with commercial considerations.
The introduction of PG-13 created ripple effects throughout the entertainment industry that continue to influence filmmaking today. The rating became synonymous with mainstream Hollywood entertainment, shaping not only what stories were told but how they were told. Action films, superhero movies, and sci-fi blockbusters found their natural home in the PG-13 category, leading to the development of filmmaking techniques that could suggest violence and intensity without explicitly showing it.
Decades later, PG-13 remains the most sought-after rating for major studio releases, influencing everything from superhero franchises to animated features that push the boundaries of traditional family entertainment. The rating has become so embedded in Hollywood culture that it continues to shape creative decisions and audience expectations, proving that sometimes the most significant changes come from filling the gaps that others overlook.